ehv hv mv lv | CLASSIFICATION OF VOLTAGE LEVELS ehv hv mv lv Electricity generation is performed for the most efficient generation voltage for that generation type. Then usually, stepped-up to Extra-High Voltage (EHV) for transmission and this level stepped-down to High-Voltage (HV) level at the .
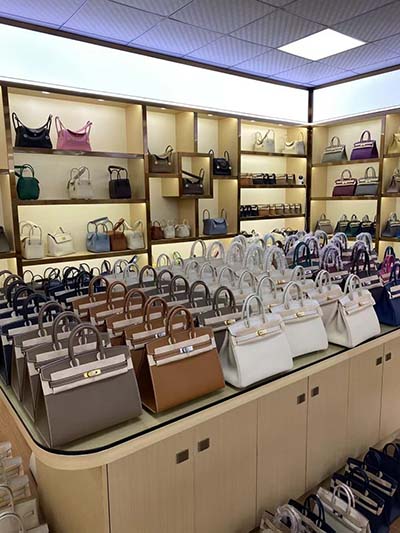
Release 5 April 2022. The story of Dior’s historic birthplace is revealed in a new book, Dior, The Legendary 30, Avenue Montaigne, published by Rizzoli New York to mark the reopening of the iconic Paris address following more than two years of renovation.DIOR Paris 30 Montaigne. Dior Boutique. 30 Avenue Montaigne. 75008 Paris. +33157961947. Categories. Women's Fashion. Ready-to-wear, Bags, Small leather .
0 · What is Considered High Voltage? HV Applications
1 · Voltages & Their Classifications
2 · Voltage Classification of LV, MV, and HV
3 · Voltage Classification of LV, MV and HV
4 · Voltage Classification
5 · Understanding HV and LV in Electrical Systems: A Guide for
6 · FAQ: Low, medium, high, extra high voltage
7 · Difference Between High, Medium & Low Voltage
8 · CLASSIFICATION OF VOLTAGE LEVELS
9 · 7 Types of Voltage Level ELV LV MV HV EHV Ultra
Dubbed 30 Montaigne in a reference to the brand's iconic address, the new bag .
High Voltage: The voltage level between 33kV to 220 kV is called High Voltage. Also, the transmission line carries the high voltages is called high voltage .

versace wr5atm vbq
As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in .It is quite common for this to be further broken down into medium voltage (MV), high voltage (HV), and extra high voltage (EHV). As we scale up, we enter the realm of medium voltage (MV), .High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site .

What is Considered High Voltage? HV Applications
There are four primary classifications of voltage levels: low (LV), medium (MV), HV, and extra HV (EHV). Ultra HV (UHV) is another classification for exceptionally high voltages, typically used in long-distance power transmission projects.Electricity generation is performed for the most efficient generation voltage for that generation type. Then usually, stepped-up to Extra-High Voltage (EHV) for transmission and this level stepped-down to High-Voltage (HV) level at the .
Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra .High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables .Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV. Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V. EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between generation and point of use. Low Voltage Classification. Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each .
Voltages & Their Classifications
Voltage Classification of LV, MV, and HV
High Voltage: The voltage level between 33kV to 220 kV is called High Voltage. Also, the transmission line carries the high voltages is called high voltage transmission lines.

As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2-Low Voltage: The voltage which does not normally exceed 250 V .
It is quite common for this to be further broken down into medium voltage (MV), high voltage (HV), and extra high voltage (EHV). As we scale up, we enter the realm of medium voltage (MV), typically ranging between 1000V and 35kV, commonly used in industrial facilities. But for large-scale power transmission, high voltage (HV) is essential.
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.There are four primary classifications of voltage levels: low (LV), medium (MV), HV, and extra HV (EHV). Ultra HV (UHV) is another classification for exceptionally high voltages, typically used in long-distance power transmission projects.Electricity generation is performed for the most efficient generation voltage for that generation type. Then usually, stepped-up to Extra-High Voltage (EHV) for transmission and this level stepped-down to High-Voltage (HV) level at the sub-transmission.Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra Low Voltage with a AC voltage less than 70 V. See article here. Electrical and Electronics Engineering site containing articles on a wide range of topics.
High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power .Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV. Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V. EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between generation and point of use. Low Voltage Classification.
Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage.High Voltage: The voltage level between 33kV to 220 kV is called High Voltage. Also, the transmission line carries the high voltages is called high voltage transmission lines.
As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2-Low Voltage: The voltage which does not normally exceed 250 V .It is quite common for this to be further broken down into medium voltage (MV), high voltage (HV), and extra high voltage (EHV). As we scale up, we enter the realm of medium voltage (MV), typically ranging between 1000V and 35kV, commonly used in industrial facilities. But for large-scale power transmission, high voltage (HV) is essential.High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.
There are four primary classifications of voltage levels: low (LV), medium (MV), HV, and extra HV (EHV). Ultra HV (UHV) is another classification for exceptionally high voltages, typically used in long-distance power transmission projects.
Voltage Classification of LV, MV and HV
Electricity generation is performed for the most efficient generation voltage for that generation type. Then usually, stepped-up to Extra-High Voltage (EHV) for transmission and this level stepped-down to High-Voltage (HV) level at the sub-transmission.Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra Low Voltage with a AC voltage less than 70 V. See article here. Electrical and Electronics Engineering site containing articles on a wide range of topics.High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power .Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV. Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V. EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between generation and point of use. Low Voltage Classification.
Voltage Classification
31 Rue Cambon Eau de Parfum by Chanel is a Woody Chypre fragrance for women. 31 Rue Cambon Eau de Parfum was launched in 2016. .
ehv hv mv lv|CLASSIFICATION OF VOLTAGE LEVELS