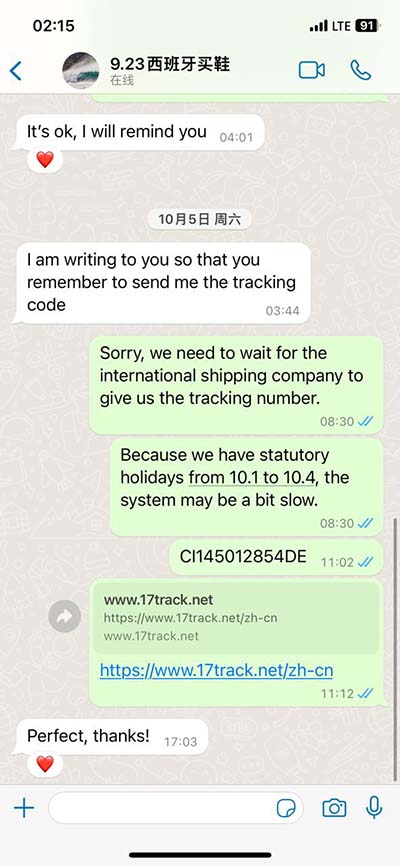
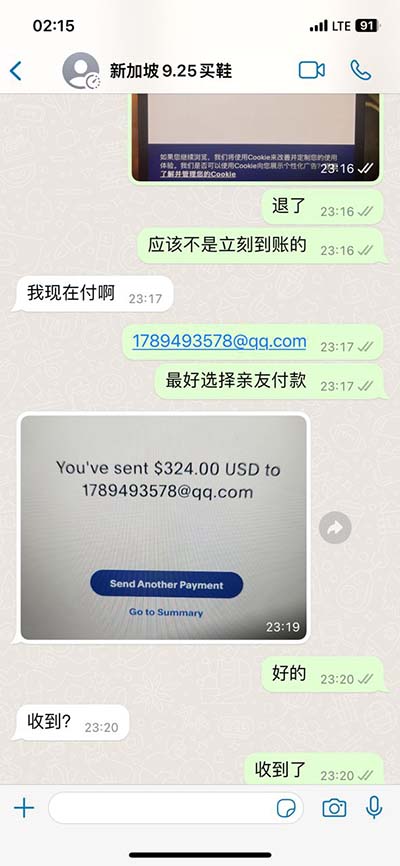
lv shorting 21 | Assessing left ventricular systolic function lv shorting 21 Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that . See more Level; Taking the Black: Ul'dah: 30: You'll Never Go Back: Ul'dah: 35: International Relations: Ul'dah: 40: The Voidgate Breathes Gloomy: Eastern Thanalan: 45: The Blood Must Flow: Eastern Thanalan: 45: Always Bet on Black: Eastern Thanalan: 50: A Relic Reborn (Stardust Rod) North Shroud: 50: Black Books: Ul'dah: 50: An Unexpected .
0 · THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
1 · Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied
2 · LV fractional shortening (FS%)
3 · LV Fractional Shortening Calculator
4 · Global Longitudinal Strain Predicts Long
5 · Fractional shortening for estimation of ejection fraction
6 · Ejection Fraction Heart Failure Measurement
7 · Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic
8 · Assessing left ventricular systolic function
9 · Assessing Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction With
Magic Action (24 AP, Magic page): Gain AP for casting spells. Armiger Action and Armiger Chain Reaction (48 AP each, Armiger page once armiger unlocks): Gain AP for activating Armiger. Our top 10.
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that . See moreAn EF from 41 to 49 percent might be considered too low. It does not always indicate that a person is developing heart failure, but it could indicate damage, perhaps from a previous heart attack. An ejection fraction measurement under 40 percent might be . See more
Your health care professional might mention one of these two EF-related scenarios: 1. Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)– also . See moreYour health care professional might recommend one or more of these tests to measure your ejection fraction: 1. Echocardiogram(or “echo”) - the most widely used test 2. . See more
LV Fractional Shortening Calculator. Determines the percentage of size reduction of the left ventricle based on M-mode measurements. Refer to the text below the tool for more .The most common views to assess for left ventricular ejection fraction are the parasternal long axis, parasternal short axis (mid-papillary level), and apical 4 chamber view. The subxiphoid .In particular, a 1-cm increase in LV wall thickness or a 100-mL decrease in LV end-diastolic volume reduced the global systolic shortening required to maintain LVEF by 3.0 and 2.1 .Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the percentage change in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is measured in parasternal long axis view (PLAX) using M-mode . .
Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women). Refer to Table 2 .
Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if .
Speckle Tracking Strain has emerged as the most useful new echocardiographic tool to assess myocardial function. Global Longitudinal Strain is best represented in the literature as being a .Run the Echocardiography Online Simulator. Choose 4 chamber position from the List <> or find 4 chamber position with 3D Transducer. Click the button <> to . Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking . A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
LV Fractional Shortening Calculator. Determines the percentage of size reduction of the left ventricle based on M-mode measurements. Refer to the text below the tool for more information about LV FS and its normal values.The most common views to assess for left ventricular ejection fraction are the parasternal long axis, parasternal short axis (mid-papillary level), and apical 4 chamber view. The subxiphoid view can also be performed with the parasternal or apical views cannot be obtained.In particular, a 1-cm increase in LV wall thickness or a 100-mL decrease in LV end-diastolic volume reduced the global systolic shortening required to maintain LVEF by 3.0 and 2.1 percentage points, respectively.Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the percentage change in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is measured in parasternal long axis view (PLAX) using M-mode . The end-systolic and end-diastolic left ventricular diameters are measured.
Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women). Refer to Table 2 (normal values for non-contrast images) and Table 4 (recommendations for the normalFractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities.Speckle Tracking Strain has emerged as the most useful new echocardiographic tool to assess myocardial function. Global Longitudinal Strain is best represented in the literature as being a sensitive measure additive to EF. Most Promising New Clinical Applications: Adding to EF in Heart Failure to Enhance Prognosis.

Run the Echocardiography Online Simulator. Choose 4 chamber position from the List <> or find 4 chamber position with 3D Transducer. Click the button <> to freeze image. Using Slider find LV End-Systolic frame. Click Button <> Click Tab <> Click Radio Button <>. Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking echocardiography. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
LV Fractional Shortening Calculator. Determines the percentage of size reduction of the left ventricle based on M-mode measurements. Refer to the text below the tool for more information about LV FS and its normal values.The most common views to assess for left ventricular ejection fraction are the parasternal long axis, parasternal short axis (mid-papillary level), and apical 4 chamber view. The subxiphoid view can also be performed with the parasternal or apical views cannot be obtained.
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied
In particular, a 1-cm increase in LV wall thickness or a 100-mL decrease in LV end-diastolic volume reduced the global systolic shortening required to maintain LVEF by 3.0 and 2.1 percentage points, respectively.
Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the percentage change in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is measured in parasternal long axis view (PLAX) using M-mode . The end-systolic and end-diastolic left ventricular diameters are measured.Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women). Refer to Table 2 (normal values for non-contrast images) and Table 4 (recommendations for the normal

LV fractional shortening (FS%)
Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities.
LV Fractional Shortening Calculator
Speckle Tracking Strain has emerged as the most useful new echocardiographic tool to assess myocardial function. Global Longitudinal Strain is best represented in the literature as being a sensitive measure additive to EF. Most Promising New Clinical Applications: Adding to EF in Heart Failure to Enhance Prognosis.Run the Echocardiography Online Simulator. Choose 4 chamber position from the List <> or find 4 chamber position with 3D Transducer. Click the button <> to freeze image. Using Slider find LV End-Systolic frame. Click Button <> Click Tab <> Click Radio Button <>.
Global Longitudinal Strain Predicts Long
 .jpg)
Requirements. 071341.png60A Striking Opportunity A Striking Opportunity (Level 60) 071201.png80Shadowbringers Shadowbringers (Level 80) Disciples of War or Magic (Level 80) Rewards. 575. Miscellaneous Reward. Unlocks .
lv shorting 21|Assessing left ventricular systolic function